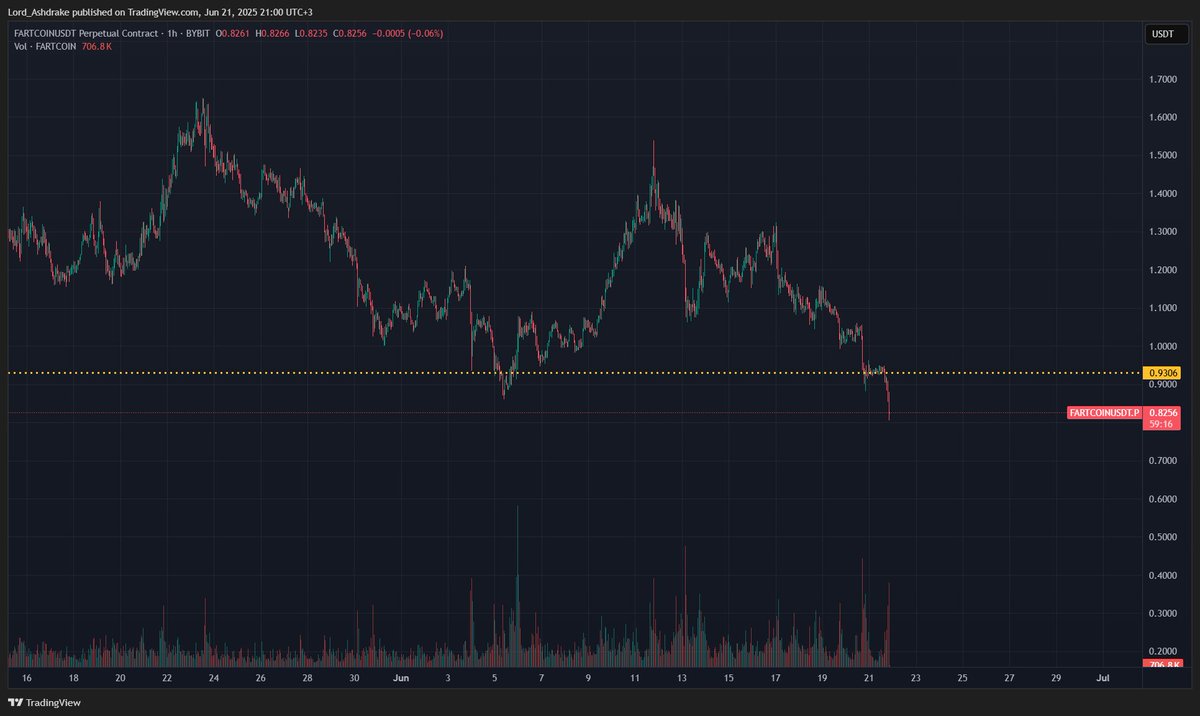
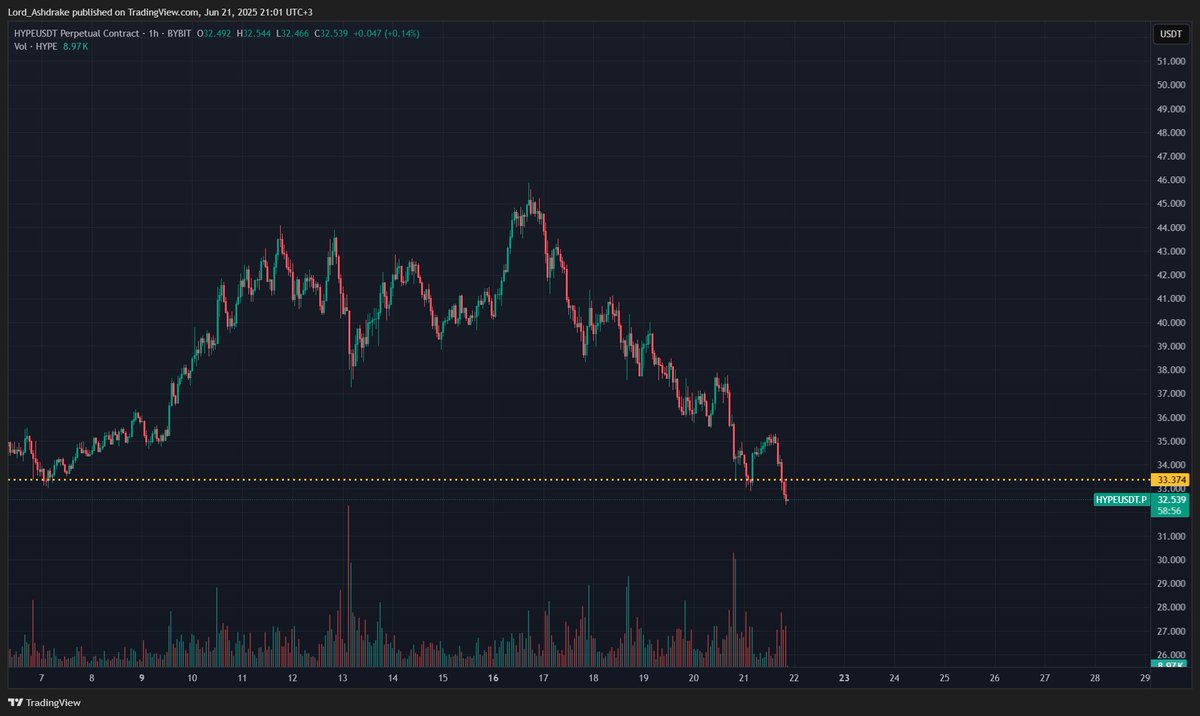
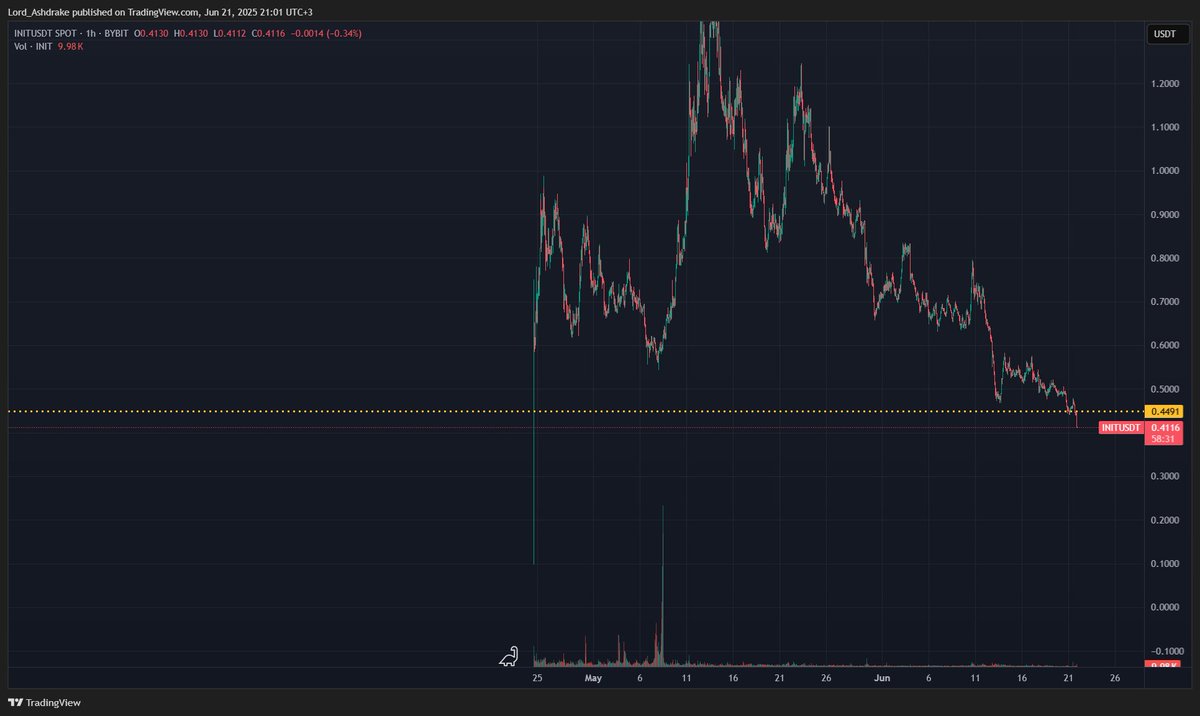
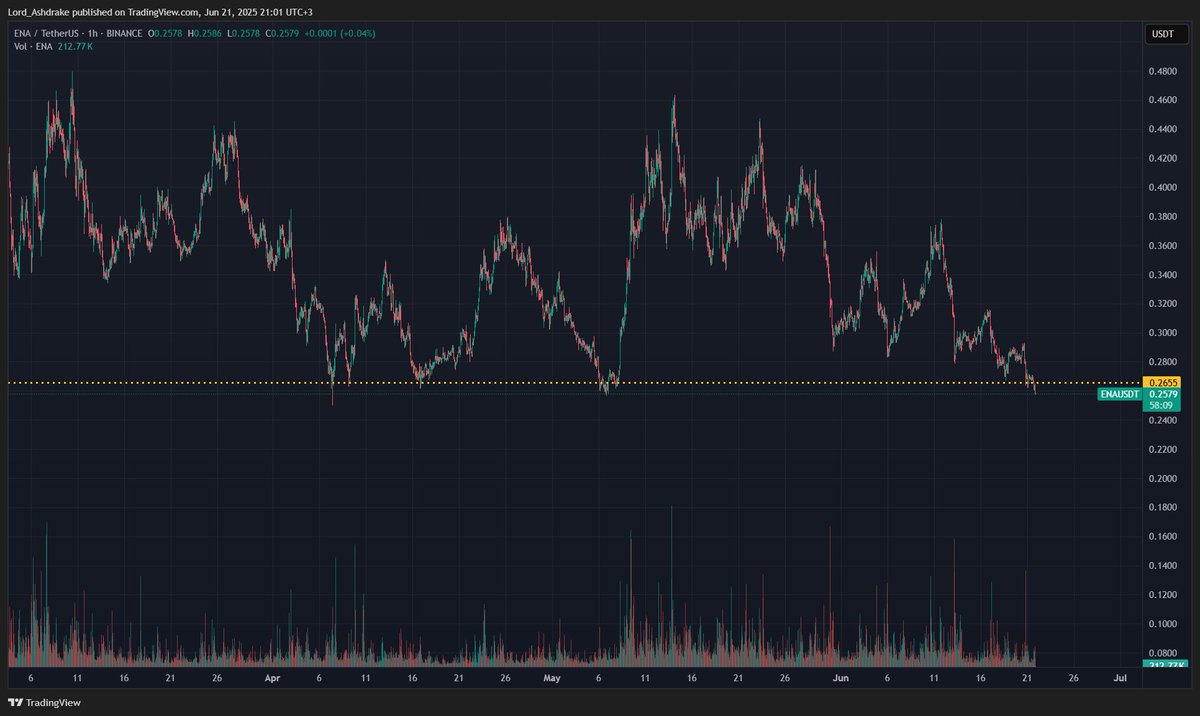
Prezzo di Lido DAO

Disclaimer
OKX non fornisce raccomandazioni su investimenti o asset. Devi considerare attentamente se il trading o l'holding di asset digitali è adatto a te alla luce della tua condizione finanziaria. Consulta un professionista legale/fiscale/finanziario per domande sulla tua specifica situazione. Per ulteriori dettagli, fai riferimento ai nostri Termini di utilizzo e all'Avviso di rischio. Utilizzando il sito web di terze parti ("TPW"), accetti che qualsiasi utilizzo del TPW sarà soggetto alle condizioni del TPW e disciplinato dalle stesse. Se non espressamente dichiarato per iscritto, OKX e i suoi affiliati ("OKX") non sono associati in alcun modo al proprietario o all'operatore del TPW. Accetti che OKX non è responsabile di eventuali perdite, danni e qualsiasi altra conseguenza derivanti dall'utilizzo del TPW. Tieni presente che l'uso di un TPW potrebbe comportare una perdita o una diminuzione dei tuoi asset. Il prodotto potrebbe non essere disponibile in tutte le giurisdizioni.
Informazioni sul mercato di Lido DAO
Capitalizzazione di mercato = Offerta circolante x Ultimo prezzo

Feed di Lido DAO





Calcolatore LDO


Prestazioni prezzo Lido DAO in USD
Conversioni di Lido DAO popolari
| 1 LDO in USD | 0,64320 $ |
| 1 LDO in EUR | 0,55812 € |
| 1 LDO in PHP | 36,7730 ₱ |
| 1 LDO in IDR | 10.559,84 Rp |
| 1 LDO in GBP | 0,47911 £ |
| 1 LDO in CAD | 0,88410 $ |
| 1 LDO in AED | 2,3622 AED |
| 1 LDO in VND | 16.806,90 ₫ |
Informazioni su Lido DAO (LDO)
- Sito web ufficiale
- White paper
- Github
- Block explorer
Domande frequenti relative al prezzo di Lido DAO
Lido è un protocollo decentralizzato che offre servizi di liquid staking per varie blockchain Proof of Stake (PoS). Quando gli utenti mettono in staking asset su Lido, ricevono equivalenti tokenizzati dei loro token messi in staking su base 1:1. Questi token rimangono liquidi, consentendo agli utenti di utilizzarli su varie piattaforme.
Lido applica una commissione del 10% sulle ricompense da staking. Nonostante sia visto da alcuni come uno svantaggio, questo tasso si allinea strettamente agli standard del settore, mantenendo Lido competitivo.
Esegui l'acquisto dei token LDO sulla piattaforma di criptovalute OKX. Il terminale di trading spot di OKX include la coppia di trading LDO/USDT.
Potete anche scambiare le vostre criptovalute esistenti, tra cui XRP (XRP), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), e Chainlink (LINK), con LDO senza commissioni e senza slittamenti di prezzo utilizzando OKX Convert.
Informativa ESG
Calcolatore LDO