Prezzo: Polkadot
in USD

Informazioni su Polkadot
Disclaimer
OKX non fornisce raccomandazioni su investimenti o asset. Devi considerare attentamente se il trading o l'holding di asset digitali è adatto a te alla luce della tua condizione finanziaria. Consulta un professionista legale/fiscale/finanziario per domande sulla tua specifica situazione. Per ulteriori dettagli, fai riferimento ai nostri Termini di utilizzo e all'Avviso di rischio. Utilizzando il sito web di terze parti ("TPW"), accetti che qualsiasi utilizzo del TPW sarà soggetto alle condizioni del TPW e disciplinato dalle stesse. Se non espressamente dichiarato per iscritto, OKX e i suoi affiliati ("OKX") non sono associati in alcun modo al proprietario o all'operatore del TPW. Accetti che OKX non è responsabile di eventuali perdite, danni e qualsiasi altra conseguenza derivanti dall'utilizzo del TPW. Tieni presente che l'uso di un TPW potrebbe comportare una perdita o una diminuzione dei tuoi asset. Il prodotto potrebbe non essere disponibile in tutte le giurisdizioni.
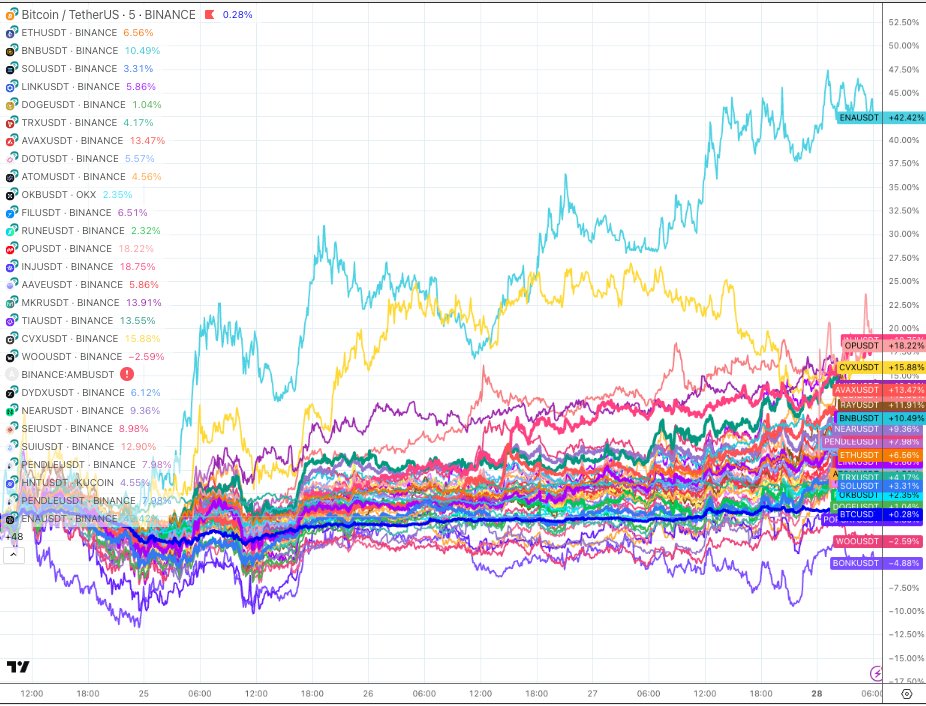
Prestazioni prezzo Polkadot
Polkadot sui social


Guide

Crea un conto OKX gratuito.
Finanzia il tuo conto.
Scegli la criptovaluta.
Domande frequenti relative al prezzo di Polkadot
OKX offre diversi modi per richiedere assistenza. Il nostro self-servicecentro assistenzarisponde alle domande frequenti sull'acquisto, la vendita e il trading di asset digitali. Inoltre, abbiamo una community globale molto attiva con cui è possibile entrare in contatto tramite vari canali, tra cui Telegram, Reddit, Facebook, Line, Weibo e Twitter.
Esplora Polkadot
Spesso definita la "blockchain delle blockchain", Polkadot è un metaprotocollo di layer 0 di nuova generazione e una blockchain open source lanciata nel maggio 2020 per realizzare la visione più ampia di una blockchain sicura, resiliente ed equa Web3.
Polkadot riunisce una rete di blockchain native di layer 1, note come parachain, e molteplici blockchain esterne (collegate a questa rete grazie a un'innovativa tecnologia di bridging), consentendo loro di operare in scala senza soluzione di continuità l'una accanto all'altra.
Le parachain e le blockchain esterne possono interagire liberamente tra loro, rendendole interoperabili. Si tratta di una svolta importante rispetto alla struttura a compartimenti stagni delle blockchain tradizionali Ethereum e Bitcoin.
Le parachain possono elaborare transazioni simultaneamente, riducendo il carico sulla catena principale e facilitando la scalabilità. Inoltre, consentono agli sviluppatori di personalizzare le loro blockchain, permettendo loro di ottimizzare le parachain per casi d'uso specifici con i loro token nativi.
La catena relay è la catena centrale di Polkadot, creata utilizzando il framework Substrate. La catena relay è responsabile del mantenimento della sicurezza condivisa di Polkadot, dell'interoperabilità tra le catene e del meccanismo di consenso. È stata progettata per gestire funzioni minime, tra cui la governance della rete e la Named Proof of Stake (NPoS). Tutti i validatori sono collegati alla catena relay e confermano le transazioni delle paracatene collegate.
L'ecosistema Polkadot comprende anche i parathread, che sono parachain basati su un modello pay-per-use, che li rende più accessibili. Le parachain e i parathread possono connettersi e comunicare con blockchain esterne come Bitcoin o Ethereum tramite bridge.
La rete è protetta dal meccanismo di consenso NPoS. Gli utenti possono scegliere di partecipare al sistema di consenso come nominatori o validatori. I nominatori possono selezionare validatori fidati per aggiornare la rete, mentre i validatori verificano le transazioni. Nominatori e validatori fanno stake su DOT e ricevere in cambio ricompense.
Casi d'uso di DOT
Il DOT ha molteplici funzioni all'interno dell'ecosistema Polkadot. È la valuta utilizzata per pagare le commissioni di transazione quando si inviano dati o token tra i canali. Serve anche come gettone di governance che gli utenti possono mettere in gioco per votare sul futuro di Polkadot.
I token DOT sono utilizzati anche come valuta per incoraggiare gli utenti a mantenere la sicurezza del sistema. Gli utenti possono puntare i DOT per partecipare al meccanismo di consenso della rete. I DOT sono utilizzati anche per il bonding, un tipo di Proof of Stake. Con il bonding dei token, gli sviluppatori possono creare nuove paracatene, mentre la rimozione degli asset bondati rimuove le paracatene obsolete.
Tokenomics e distribuzione di DOT
Il DOT è un token inflazionistico, il che significa che non ha un tetto o un'offerta massima. Il suo tasso di inflazione è di circa il 10%, con la generazione di nuovi gettoni per incoraggiare i validatori. I DOT possono essere trasferiti in frazioni, l'unità più piccola è 0,0000000001 DOT, nota come Planck.
10 milioni di token DOT sono stati generati in occasione della prima offerta iniziale di monete (ICO) tenutasi nell'ottobre 2017. I token sono stati distribuiti come segue:
- 50 per cento: acquirenti dell'ICO
- 30 per cento: Web3 Foundation per lo sviluppo di Polkadot e altre attività della Fondazione.
- 11,6 per cento: Fondazione Web3 per future iniziative di raccolta fondi
- 5 per cento: vendita privata nel 2019
- 3,4%: Vendita di token nel 2020
Il 21 agosto 2020 ha avuto luogo un rebranding di DOT, a seguito di un referendum a livello di rete. Di conseguenza, il saldo DOT di tutti i titolari esistenti è stato automaticamente aumentato di 100 volte. L'offerta iniziale di 10 milioni di DOT è passata a 1 miliardo dopo la ridenominazione e il valore di mercato di ciascun token DOT è diminuito di un fattore 100. Questo evento è noto come "Giorno della denominazione".
Informazioni sui fondatori
Polkadot è il progetto di punta della Web3 Foundation, costituita da Gavin Wood, Peter Czaban e Robert Habermeier nel 2017. La Web3 Foundation è una fondazione senza scopo di lucro con sede in Svizzera, creata per sostenere gli sforzi di ricerca, sviluppo e raccolta fondi di Polkadot.
Ben noto nel mondo delle criptovalute e della blockchain, Wood è uno dei pionieri della tecnologia blockchain. È il cofondatore ed ex CTO di Ethereum e fondatore di Parity Technologies. Inoltre, Wood ha coniato il termine Web3 nel 2014.
Wood ha anche inventato Whisper, un P2P communication protocol, il consenso Proof of Authority e il linguaggio di programmazione Solidity. Attualmente dirige le iniziative di innovazione di Polkadot e Substrate.
Czaban ha conseguito un master in ingegneria presso l'Università di Oxford e ha co-fondato la Web3 Foundation e Polkadot con Wood. In qualità di CTO della Web3 Foundation, Czaban sostiene la creazione di tecnologie distribuite di nuova generazione.
Habermeier è un Thiel Fellow con una vasta esperienza di ricerca e sviluppo nella crittografia, nei sistemi distribuiti e nella tecnologia blockchain. Membro di lunga data della comunità Rust, Habermeier è anche noto per l'utilizzo di Rust per sviluppare soluzioni parallele e ad alte prestazioni.
Informativa ESG