Preço de Uniswap
em USD

Sobre Uniswap
Aviso legal
A OKX não fornece recomendações de investimentos ou de ativos. Deve ponderar cuidadosamente se fazer trading ou deter ativos digitais é o mais adequado para si, tendo em conta a sua situação financeira. Informe-se junto do seu consultor jurídico/fiscal/de investimentos para esclarecer questões relativas às suas circunstâncias específicas. Para obter mais detalhes, consulte os nossos Termos de Utilização e o Aviso de Risco. Ao utilizar o site de terceiros ("TPW"), aceita que qualquer utilização do TPW está sujeita e será regida pelos termos do TPW. Salvo indicação expressa por escrito, a OKX e os seus afiliados ("OKX") não estão, de forma alguma, associados ao proprietário ou operador do TPW. Concorda que a OKX não é responsável nem imputável por quaisquer perdas, danos e outras consequências que advenham da sua utilização do TPW. Tenha presente que utilizar um TPW poderá resultar na perda ou diminuição dos seus ativos. O produto poderá não estar disponível em todas as jurisdições.
Desempenho do preço de Uniswap
Uniswap nas redes sociais


Guias

Crie uma conta OKX gratuita.
Financie a sua conta.
Escolha a sua cripto.
Perguntas frequentes sobre Uniswap
Explora as Uniswap de forma mais detalhada
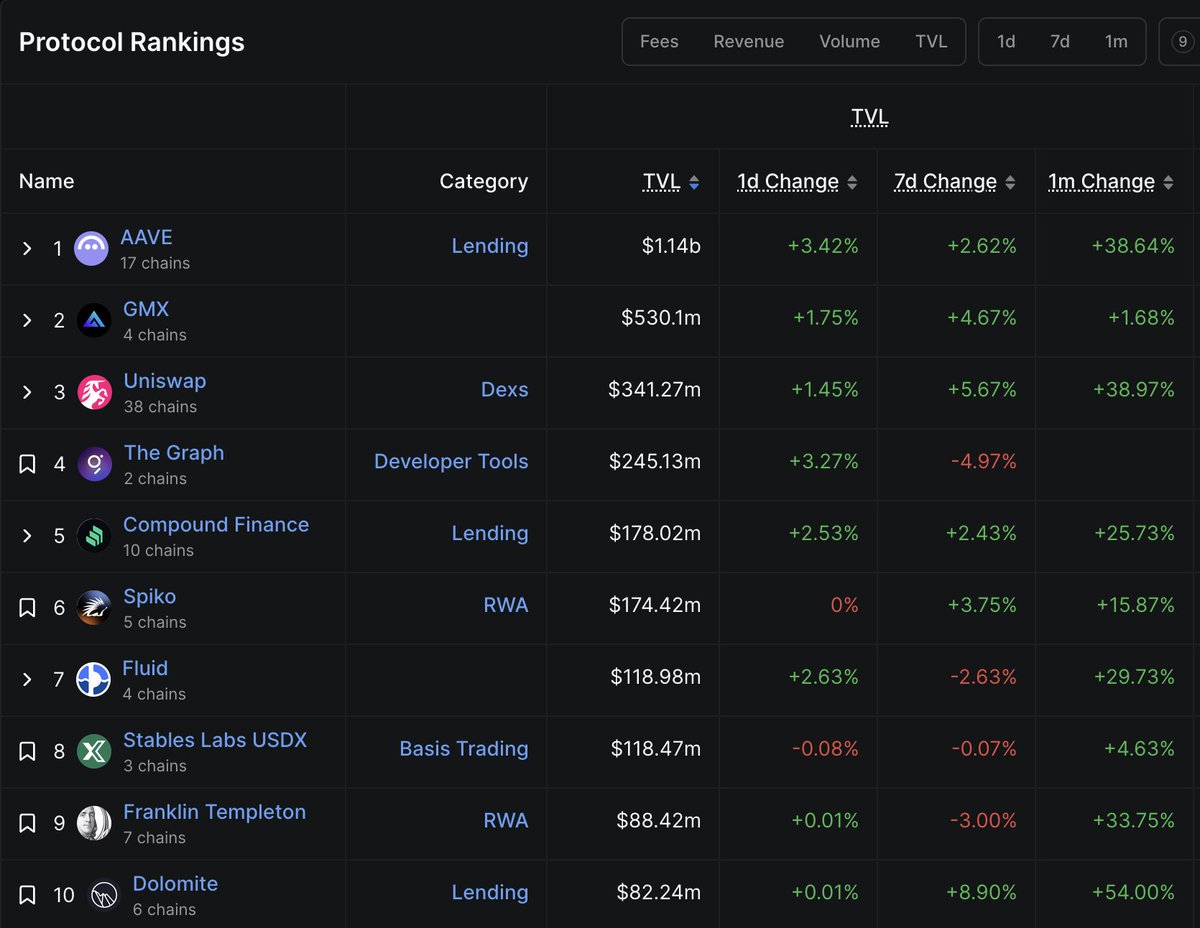
A Uniswap é uma bolsa descentralizada, comumente chamada de DEX, desenvolvida na blockchain Ethereum. Os traders usam a Uniswap paratrocar tokens ERC-20 de imediatosem a necessidade de um mercado líquido de compradores, vendedores ou intermediários. A rede prioriza a resistência à censura, a segurança e a custódia automática sem a necessidade de intermediários de terceiros.
Ao contrário de uma bolsa centralizada que processa ordens de transação interna através de um Livro de ordens, umaa exchange descentralizada opera um criador de mercado automático (AMM), que funciona como um pool de liquidez constante e sem permissões, o qual os traders podem interagir diretamente on-chain. O UNI é o token nativo do protocolo Uniswap e está disponível para ser transacionado em vários mercados na OKX. O UNI tem de votar em propostas que regem o desenvolvimento da plataforma Uniswap. Também pode utilizar o UNI para criar pares de liquidez e ganhar recompensas em criptomoeda.
O ecossistema Uniswap consiste nas seguintes funcionalidades:
- Uniswap Labs: a empresa que desenvolveu o protocolo Uniswap.
- O Uniswap Protocol: uma bolsa de criptomoedas descentralizada na blockchain Ethereum.
- A interface Uniswap: uma interface web que permite aos utilizadores interagir com o protocolo.
- Governação Uniswap: um sistema de governação que utiliza o token UNI para governar o protocolo Uniswap.
Embora inicialmente desenvolvido para a rede Ethereum, o Uniswap está agora operacional naPolygon,Arbitrume blockchains Optimism. Esta flexibilidade cross-chain é uma das coisas que os utilizadores de finanças descentralizadas adoram no Uniswap.
Como funciona o Uniswap?
A Uniswap é uma plataforma de exchange descentralizada que facilita a criação de uma enorme variedade de pools de liquidez que os traders podem usar para fazer swap de tokens. Qualquer token compatível pode ser adicionado a uma DEX e negociado sem que seja necessária uma entidade ou negócio centralizado para alojar a exchange.
Para ativar isto,O Uniswap usa contratos inteligentes, uma utilidade essencial nas finanças descentralizadas, para permitir que os traders troquem tokens através de um criador de mercado automatizado. Um criador de mercado automático, como o Uniswap, é um meio de troca que permitirá aos traders fazer swap de criptomoedas em pools de liquidez na blockchain através da aplicação na web do Uniswap. Ao usar o Uniswap, os utilizadores não se limitam por fatores externos, como os horários de abertura do mercado e a necessidade de outros traders criarem ordens correspondentes.
Para criar um pool de liquidez, um fornecedor de liquidez deve fornecer dois tokens diferentes que podem se tornar um pool de tokens partilhados que os utilizadores do Uniswap podem transacionar. O preço dos tokens num pool de liquidez específico é regulado por uma fórmula matemática que dita o valor dos tokens. O trading com um pool de liquidez altera o rácio dos tokens dentro do pool, provocando alterações ao preço de cada token.
As taxas de transação incentivam os fornecedores de liquidez a fornecer tokens a um pool de liquidez Uniswap. Os fornecedores recebem uma percentagem de todas as transações que trocam tokens com o pool.Aplicação descentralizada (DApp) Uniswapfacilita a criação de uma enorme variedade de pools de liquidez que os traders podem usar para fazer swap de tokens. Qualquer token compatível pode ser adicionado ao Uniswap e negociado sem que seja necessária uma entidade ou negócio centralizado para alojar o mercado.
Preço e economia de tokens do UNI
O UNI é umToken ERC-20 com uma oferta em circulaçãode cerca de 734 000 000 e uma oferta máxima original de 1000 000 000 tokens. Estes tokens serão distribuídos da seguinte forma ao longo de quatro anos:
- Membros da comunidade Uniswap: 60,00% (600 000 UNI).
- Colaboradores atuais e futuros: 21,266% (212 660 000 UNI).
- Investidores: 18,044% (180,440 000 UNI).
- Consultores: 0,69% (6 900 000 UNI).
15% do total da oferta de UNI foram imediatamente disponibilizados a "utilizadores históricos e fornecedores de liquidez". Isto foi feito para recompensar os membros iniciais da comunidade pela sua confiança na rede e liquidez. Além disso, 43% dos tokens de UNI serão detidos pela tesouraria de governação do Uniswap. Estes 430 000 000 tokens serão distribuídos através de doações dos contribuidores, iniciativas da comunidade, mineração de liquidez e outros programas.
A oferta de UNI é inflacionária, seguindo uma taxa de 2%, a partir de quatro anos após a cunhagem do token. Este modelo inflacionário garante a participação e contribuição contínua para a rede Uniswap. A estrutura de emissão do Uniswap indica que a oferta total máxima será atingida em setembro de 2024.
Sobre o fundador
O desenvolvimento do protocolo Uniswap começou em 2017 quando o fundador Hayden Adams foi afastado do seu cargo de engenheiro mecânico na Siemens. Adams contactou o seu amigo Karl Floersch, que sugeriu saber mais sobre Ethereum e contratos inteligentes. Para desenvolver as suas competências de programação e aprender mais sobre a tecnologia de blockchain, Adams começou a trabalhar num projeto queVitalik Buterin, o fundador da Ethereum, tinha descrito no Reddit, um fórum online popular.
Adams foi completamente cativado pelas crenças que levaram ao projeto Ethereum. As missões de descentralização e protocolos de permissão levaram-no a continuar a desenvolver a plataforma Uniswap, apesar de estar desempregado na altura. Ocorreu um enorme avanço em abril de 2018, quando Adam foi apresentado a Vitalik Buterin na conferência da Determ, em Seul. Buterin leu o código fonte de Adam e aconselharam-no a candidatar-se a uma bolsa da Ethereum Foundation e a continuar a desenvolver o Uniswap numa linguagem diferente.
Após vários meses de desenvolvimento contínuo, a bolsa descentralizada Uniswap foi finalmente implementada na rede principal Ethereum, em novembro de 2018. No entanto, a equipa não parou por aqui e, até hoje, continua a melhorar a plataforma com atualizações frequentes. Um exemplo disso são os escalões de taxas de transação opcionais no Uniswap V3. Isto permite aos fornecedores de liquidez escolherem quanto traders precisam para pagar em taxas de transação durante o trading. Hoje em dia, o Uniswap detém o valor total mais alto bloqueado (TV) em qualquer exchange descentralizada maior blockchain de contrato inteligente de camada 1na indústria das criptomoedas.
Como pioneiro neste ramo, o Uniswap atraiu um interesse significativo junto de vários investidores institucionais conhecidos, como a Delphi Digital, Pantera Capital, a16z Crypto e o Blockchain Capital, que apoiavam e financiavam o Uniswap. Estes fundos experientes ajudaram no desenvolvimento do Uniswap e são um contributo significativo para o seu sucesso atual.
Destaques do Uniswap
NFTs no Uniswap
Um dos desenvolvimentos mais emocionantes e discutidos que se aproxima do Uniswap é a integraçãoum agregador de tokens não fungíveis (NFT)para a plataforma. Em junho de 2022, a Uniswaps Labs anunciou que adquiriu o Genie e que o implementaria no site da Uniswap.
A Genie é um agregador de NFT. Isto significa que os potenciais compradores de NFT podem usar a Genie para colecionar e comprar NFT listados em qualquer mercado, tudo num único lugar. Isto simplifica o processo de recolha de NFT e elimina a necessidade de verificar muitos mercados diferentes para os melhores preços. Este é um passo enorme no desenvolvimento do projeto, resultando no entusiasmo dos utilizadores e colecionadores de NFT DeFi relativamente à Uniswap.
The Swap Widget
Em abril de 2022, o desenvolvimento do Uniswap lançou o Swap Widget, uma função de swap simples que os programadores poderiam facilmente integrar nas suas aplicações. O Swap Widget permite aos utilizadores transacionar tokens a partir de um site de terceiros em vez de navegar para a aplicação web do Uniswap. O Swap Widget pode ser adicionado a uma dApp compatível através de apenas uma linha de código e já está a ser utilizado por sites populares como o OpenSea.
Divulgação ASG