
DAI
DAI koers
$1,0001
+$0,000100000
(+0,00%)
Prijsverandering voor de afgelopen 24 uur

Wat vind je vandaag van DAI?
Deel je mening hier door een duim omhoog te geven als je je bullish voelt over een munt of een duim omlaag als je je bearish voelt.
Stem om resultaten te bekijken
Disclaimer
De sociale inhoud op deze pagina ("Inhoud"), inclusief maar niet beperkt tot tweets en statistieken die door LunarCrush worden verstrekt, is afkomstig van derden en wordt alleen voor informatieve doeleinden geleverd "zoals deze is". OKX geeft geen garantie voor de kwaliteit of nauwkeurigheid van de Inhoud en de Inhoud vertegenwoordigt niet de standpunten van OKX. Het is niet bedoeld om (i) beleggingsadvies of een beleggingsaanbeveling te geven; (ii) een aanbod of verzoek om digitale bezitting te kopen, verkopen of te bezitten; of (iii) financieel, boekhoudkundig, juridisch of fiscaal advies. Digitale bezittingen, waaronder stablecoins en NFT's, brengt een hoog risico met zich mee en kan sterk fluctueren. De prijs en prestaties van de digitale bezittingen zijn niet gegarandeerd en kunnen zonder voorafgaande kennisgeving worden gewijzigd.
OKX geeft geen beleggings- of vermogensadvies. Je moet zorgvuldig overwegen of het verhandelen of bezitten van digitale bezittingen voor jou geschikt is in het licht van je financiële toestand. Raadpleeg je juridische, fiscale of beleggingsadviseur als je vragen hebt over je specifieke situatie. Raadpleeg voor meer informatie onze Gebruiksvoorwaarden en Risicowaarschuwing. Door gebruik te maken van de website van derden ('TPW'), ga je ermee akkoord dat elk gebruik van de TPW onderworpen is aan en beheerst wordt door de voorwaarden van de TPW. Tenzij uitdrukkelijk schriftelijk vermeld, zijn OKX en haar partners ("OKX") op geen enkele manier verbonden met de eigenaar van de exploitant van de TPW. Je gaat ermee akkoord dat OKX niet verantwoordelijk of aansprakelijk is voor verlies, schade en andere gevolgen die voortvloeien uit jouw gebruik van de TPW. Houd er rekening mee dat het gebruik van een TPW kan leiden tot verlies of vermindering van je bezittingen. Het product is mogelijk niet in alle rechtsgebieden beschikbaar.
OKX geeft geen beleggings- of vermogensadvies. Je moet zorgvuldig overwegen of het verhandelen of bezitten van digitale bezittingen voor jou geschikt is in het licht van je financiële toestand. Raadpleeg je juridische, fiscale of beleggingsadviseur als je vragen hebt over je specifieke situatie. Raadpleeg voor meer informatie onze Gebruiksvoorwaarden en Risicowaarschuwing. Door gebruik te maken van de website van derden ('TPW'), ga je ermee akkoord dat elk gebruik van de TPW onderworpen is aan en beheerst wordt door de voorwaarden van de TPW. Tenzij uitdrukkelijk schriftelijk vermeld, zijn OKX en haar partners ("OKX") op geen enkele manier verbonden met de eigenaar van de exploitant van de TPW. Je gaat ermee akkoord dat OKX niet verantwoordelijk of aansprakelijk is voor verlies, schade en andere gevolgen die voortvloeien uit jouw gebruik van de TPW. Houd er rekening mee dat het gebruik van een TPW kan leiden tot verlies of vermindering van je bezittingen. Het product is mogelijk niet in alle rechtsgebieden beschikbaar.
DAI marktinformatie
Marktkapitalisatie
Marktkapitalisatie wordt berekend door het circulerende aanbod van een munt te vermenigvuldigen met de laatste prijs.
Marktkapitalisatie = Circulerend aanbod × Laatste prijs
Marktkapitalisatie = Circulerend aanbod × Laatste prijs
Circulerend aanbod
Totale bedrag van een munt dat openbaar beschikbaar is op de markt.
Positie marktkapitalisatie
De positie van een munt in termen van marktkapitalisatie.
Historisch hoogtepunt
Hoogste prijs die een munt heeft bereikt in zijn handelsgeschiedenis.
Historisch dieptepunt
Laagste prijs die een munt heeft bereikt in zijn handelsgeschiedenis.
Marktkapitalisatie
$3,70B
Circulerend aanbod
3.702.684.213 DAI
100,00% van
3.702.684.213 DAI
Positie marktkapitalisatie
27
Audits

Laatste audit: 1 mei 2021, (UTC+8)
24u hoog
$1,0002
24u laag
$0,99540
Historisch hoogtepunt
$8.976,00
-99,99% (-$8.975,00)
Laatste update: 2 aug 2019, (UTC+8)
Historisch dieptepunt
$0,0011000
+90.818,18% (+$0,99900)
Laatste update: 2 aug 2019, (UTC+8)
DAI Feed
De volgende inhoud is afkomstig van .

常为希 |加密保安🔸🚢🇺🇸
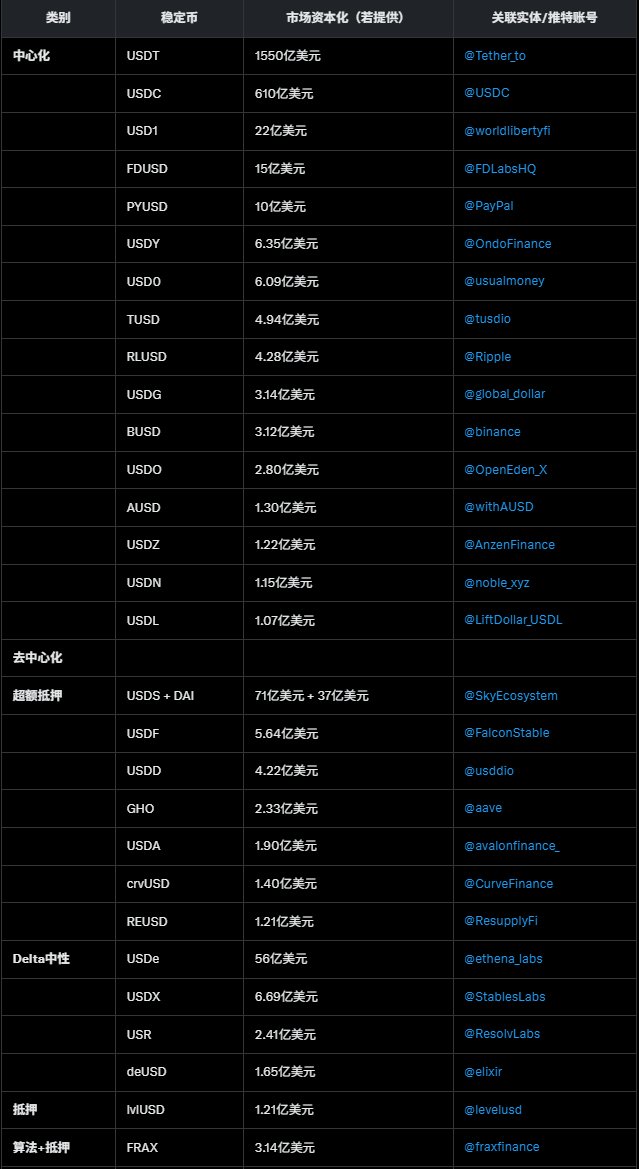
De marktkapitalisatie (MC) van stablecoins die meer dan 100 miljoen dollar bedraagt, is geclassificeerd in gecentraliseerde en gedecentraliseerde stablecoins, waarbij de gedecentraliseerde categorie verder is onderverdeeld in overgecollateraliseerd, delta-neutraal, collateralized en algoritmisch + collateralized categorieën.
De totale marktkapitalisatie van gecentraliseerde stablecoins is duidelijk hoger dan die van gedecentraliseerde stablecoins.
USDT (155 miljard dollar) en USDC (61 miljard dollar) domineren en samen beheersen ze het grootste deel van de gecentraliseerde stablecoin-markt (ongeveer 85%).
Andere gecentraliseerde stablecoins (zoals USD1, FDUSD, PYUSD, enz.) hebben een marktkapitalisatie tussen de 100 miljoen en 2,2 miljard dollar, wat aantoont dat ook kleinere projecten proberen de markt te betreden. PYUSD (1 miljard dollar) van PayPal geeft aan dat traditionele financiële reuzen beginnen in te stappen in de wereld van stablecoins.
Overgecollateraliseerd: vertegenwoordigd door USDS+DAI (7,1 miljard + 3,7 miljard dollar), deze categorie vertrouwt op overgecollateraliseerde crypto-activa (zoals ETH) om stabiliteit te behouden, met een redelijk evenwichtige marktkapitalisatieverdeling.
Delta-neutraal: USDe (5,6 miljard dollar) leidt, dit mechanisme bereikt prijsstabiliteit via hedgingstrategieën (zoals perpetual futures) en heeft een hoge kapitaal efficiëntie.
De totale marktkapitalisatie van gecentraliseerde stablecoins overschrijdt ver die van gedecentraliseerde stablecoins, wat aangeeft dat de huidige markt meer geneigd is naar door instellingen ondersteunde stabiele oplossingen.
De gediversifieerde mechanismen van gedecentraliseerde stablecoins, delta-neutraal en algoritmisch stabiel, tonen het potentieel voor technologische innovatie.
8,92K
0

DaDa | 蓝鸟会🕊️
【Spark en MakerDAO: geen bijproduct, maar een structurele verdeling van on-chain financiën】
Veel mensen beschouwen Spark als een "subprotocol" van MakerDAO, maar vanuit het perspectief van governance, productstructuur en financiële functies lijkt het meer op een "business platform" binnen het financiële ecosysteem van MakerDAO - verantwoordelijk voor de daadwerkelijke kapitaaloperaties en het dienen van de stablecoin-ecosystemen.
Het bestaan van Spark is een echte weerspiegeling van de "modularisatie" trend in on-chain financiële infrastructuur.
I. Structuurverdeling: drie lagen met elk een eigen rol
We kunnen MakerDAO, Sky Protocol en Spark beschouwen als een drie-laags structuur van on-chain: "Centraal - Platform - Frontlinie":
(1) MakerDAO: verantwoordelijk voor de uitgifte van DAI, het opstellen van rentebeleid en systematische governance, is de "centrale bank" van het hele systeem.
(2) Sky Protocol: verantwoordelijk voor het opzetten van het governance-kader van het protocol, het vaststellen van governance-parameters en het coördineren van onderliggende protocollen, is de rol van "toezicht + financiën".
(3) Spark: als DeFi-protocol onder het beheer van Sky, biedt het leningen, sparen en liquiditeitsbeheer, en fungeert als de rol van "commerciële bank", direct gericht op gebruikers en activa-stromen.
II. Kernkoppelingmechanismen
Spark opereert niet onafhankelijk; de relatie met MakerDAO komt tot uiting in meerdere kernaspecten:
(1) Rente-koppeling: de spaarmodule van Spark verwijst direct naar de DSR (DAI Saving Rate) als basisrente, en blijft in sync met Maker.
(2) Synchronisatie van onderpandstructuur: de meeste activatypes die door Spark worden ondersteund, zijn afkomstig uit het risicoparametersysteem van Maker, en erven zijn liquidatiemodel en risicobepalingslogica.
(3) Delen van governance-mechanismen: hoewel Spark nog niet volledig gebruikmaakt van SPK-governance, worden de huidige governance-beslissingen uitgevoerd door Sky, met gebruik van Maker-achtige voorstellen en parameterinstellingsprocessen.
(4) Koppeling van beveiligingsmodules: belangrijke componenten zoals het Oracle-module, de bron van de oracle en het liquidatiemechanisme zijn gedeeltelijk geleend van het Maker-systeem, wat de onderliggende stabiliteit waarborgt.
III. Samenvatting: Spark is een experimentele eenheid voor gedecentraliseerde governance in DeFi-systemen
In de traditionele financiën is "centrale bank + commerciële bank + financiële regulering" de kern van het systeem. De positie van Spark simuleert precies een soortgelijke verantwoordelijkheidsstructuur:
(1) Het draagt geen risico van geldcreatie, maar beheert daadwerkelijk rente en kapitaal;
(2) Het stelt geen systeemgovernance regels op, maar geeft feedback op echt gebruikersgedrag en gebruiksvoorkeuren;
(3) Het concurreert niet om de controle over DAI, maar kan de rente-ancrage van DAI op de blockchain direct beïnvloeden.
Spark is een diepgaande test van MakerDAO binnen een gemoduleerd financieel systeem, en het laat ons zien hoe on-chain financiën in de toekomst "macht en functie" kunnen ontkoppelen en verdelen, terwijl ze de mogelijkheid van een gecoördineerde werking van het systeem waarborgen.
@sparkdotfi @cookiedotfun #Spark #SparkFinance #COOKIE
Origineel weergeven
48,23K
139

Martain 💤🥕
🚀 @sparkdotfi Kernmechanisme-analyse
▸ Platformpositionering: Slimme toewijzing van liquiditeit aan DeFi/CeFi/RWA-markten, met transparante opbrengsten
▸ Drie kernproducten:
1. Sparen: Stort USDC/USDS/DAI, opbrengsten op elk moment opnemen (APY 5-8%)
2. SparkLend: Gedecentraliseerd leenprotocol (ondersteunt USDS/DAI als onderpand)
3. Liquiditeitslaag (ALM): Multi-chain protocol niveau kapitaal toewijzingstool
---
Gebruikershandleiding
① Maximaliseer spaaropbrengsten
→ USDC omwisselen voor USDS→ via Pendle omzetten naar YT/PT USDS (automatische rente + punten verdienen)
→ YT/PT USDS kan opnieuw worden gestaked voor leningen
② Dubbele opbrengsten uit lenen
→ Onderpand tokens lenen voor USDC/USDS/DAI
→ Gedurende de leentijd gelijktijdig opbrengsten verdienen
③ $SPK Staking-dividenden
→ Staking eerste fase airdrop tokens
→ Ontvang opbrengsten + punten + recht op tweede fase airdrop (moet worden aangehouden tot 12 augustus)
---
Technische hoogtepunten en transparantie
• SLL kapitaal toewijzingssysteem:
→ Dynamische toewijzing van reservekapitaal (gereserveerd voor opname + investering in RWA/Pendle/CeFi)
→ Real-time tracking van hoogrenderende, laagrisico activa
• Gegevens volledig openbaar:
→ Data Spark dashboard toont real-time gegevens over sparen/lenen/liquiditeitslaag
→ $SPK tokenverdeling en circulatie zijn transparant en controleerbaar
Officiële toegang:
#Spark #COOKIE @cookiedotfun
Origineel weergeven
65,81K
108
DAI prijsprestatie in USD
De huidige prijs van DAI is $1,0001. DAI ging gedurende de afgelopen 24 uur toegenomen met +0,01%. Het heeft momenteel een circulerend aanbod van 3.702.684.213 DAI en een maximaal aanbod van 3.702.684.213 DAI, waardoor het een volledig verwaterde marktkapitalisatie heeft van $3,70B. Momenteel heeft DAI positie 27 in marktkapitalisatie. De prijs van DAI/USD wordt in realtime geüpdatet.
Vandaag
+$0,000100000
+0,00%
7 dagen
+$0,00040000
+0,04%
30 dagen
+$0,00020000
+0,02%
3 maanden
+$0,000100000
+0,00%
Populaire DAI-conversies
Laatste update: 23-06-2025, 19:54
| 1 DAI tot USD | $ 1,0000 |
| 1 DAI tot EUR | € 0,87096 |
| 1 DAI tot PHP | ₱ 57,5710 |
| 1 DAI tot IDR | Rp 16.498,93 |
| 1 DAI tot GBP | £ 0,74545 |
| 1 DAI tot CAD | $ 1,3779 |
| 1 DAI tot AED | AED 3,6724 |
| 1 DAI tot VND | ₫ 26.191,72 |
Over DAI (DAI)
De beoordeling is een algehele waardering die OKX verzamelt vanaf verschillende bronnen en is alleen bestemd voor intern gebruik. OKX geeft geen garantie wat betreft de kwaliteit of de nauwkeurigheid van een beoordeling. Deze is niet bedoeld als (i) beleggingsadvies of -aanbeveling, (ii) een aanbod voor of verzoek om digitale activa te kopen, te verkopen of aan te houden, of (iii) advies op het gebied van financiën, boekhouding of belastingen. Digitale activa, waaronder stablecoins en NFT's, brengen aanzienlijke risico’s met zich mee. Ze kunnen sterk fluctueren in waarde of zelfs waardeloos worden. De prijzen en bewegingen van digitale activa zijn onvoorspelbaar en kunnen zomaar veranderen. Je digitale activa zijn niet verzekerd tegen mogelijke verliezen. In het verleden behaalde resultaten bieden geen garantie voor de toekomst. OKX garandeert geen terugbetaling van de hoofdsom of rente. OKX geeft geen aanbevelingen voor investeringen of activa. Voordat je besluit om digitale activa te verhandelen of aan te houden, moet je zorgvuldig analyseren of jouw financiële situatie dit toelaat. Raadpleeg bij vragen hierover altijd een juridisch, fiscaal of beleggingsadviseur.
Verder lezen
- Officiële website
- Whitepaper
- Blokverkenner
Informatie over websites van derden
Informatie over websites van derden
Door de website van derden ('TPW') te gebruiken, aanvaard je dat elk gebruik van de TPW onderworpen is aan en geregeld wordt door de voorwaarden van de TPW. Tenzij uitdrukkelijk schriftelijk vermeld, zijn OKX en haar partners ('OKX') op geen enkele wijze verbonden met de eigenaar of exploitant van de TPW. Je stemt ermee in dat OKX niet verantwoordelijk of aansprakelijk is voor verlies, schade en andere gevolgen die voortvloeien uit je gebruik van de TPW. Houd er rekening mee dat het gebruik van een TPW kan leiden tot verlies of waardevermindering van je bezittingen.
DAI Veelgestelde vragen
Hoe veel is één DAI vandaag waard?
Momenteel is één DAI de waarde van $1,0001. Voor antwoorden en inzicht in de prijsactie van DAI ben je op de juiste plek. Ontdek de nieuwste DAI grafieken en handel verantwoord met OKX.
Wat is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency's, zoals DAI, zijn digitale bezittingen die op een openbaar grootboek genaamd blockchains werken. Voor meer informatie over munten en tokens die op OKX worden aangeboden en hun verschillende kenmerken, inclusief live-prijzen en grafieken in real time.
Wanneer zijn cryptocurrency's uitgevonden?
Dankzij de financiële crisis van 2008 nam de belangstelling voor gedecentraliseerde financiën toe. Bitcoin bood een nieuwe oplossing door een veilige digitale bezitting te zijn op een gedecentraliseerd netwerk. Sindsdien zijn er ook veel andere tokens zoals DAI aangemaakt.
Zal de prijs van DAI vandaag stijgen?
Bekijk onze DAI Prijsvoorspellingspagina om toekomstige prijzen te voorspellen en je prijsdoelen te bepalen.
ESG-vermelding
ESG-regelgeving (Environmental, Social, and Governance) voor crypto-bezit is gericht op het aanpakken van hun milieu-impact (bijv. energie-intensieve mining), het bevorderen van transparantie en het waarborgen van ethische bestuurspraktijken om de crypto-industrie op één lijn te brengen met bredere duurzaamheids- en maatschappelijke doelen. Deze regels stimuleren de naleving van normen die risico's beperken en het vertrouwen in digitale bezitting bevorderen.
Details bezittingen
Naam
OKcoin Europe LTD
Identificatiecode relevante juridische entiteit
54930069NLWEIGLHXU42
Naam van het crypto-bezit
Dai Token
Consensusmechanisme
Dai Token is present on the following networks: binance_smart_chain, ethereum.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses a hybrid consensus mechanism called Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA), which combines elements of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA). This method ensures fast block times and low fees while maintaining a level of decentralization and security. Core Components 1. Validators (so-called “Cabinet Members”): Validators on BSC are responsible for producing new blocks, validating transactions, and maintaining the network’s security. To become a validator, an entity must stake a significant amount of BNB (Binance Coin). Validators are selected through staking and voting by token holders. There are 21 active validators at any given time, rotating to ensure decentralization and security. 2. Delegators: Token holders who do not wish to run validator nodes can delegate their BNB tokens to validators. This delegation helps validators increase their stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Delegators earn a share of the rewards that validators receive, incentivizing broad participation in network security. 3. Candidates: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are in the pool waiting to become validators. They are essentially potential validators who are not currently active but can be elected to the validator set through community voting. Candidates play a crucial role in ensuring there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, thus maintaining network resilience and decentralization. Consensus Process 4. Validator Selection: Validators are chosen based on the amount of BNB staked and votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chance of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. The selection process involves both the current validators and the pool of candidates, ensuring a dynamic and secure rotation of nodes. 5. Block Production: The selected validators take turns producing blocks in a PoA-like manner, ensuring that blocks are generated quickly and efficiently. Validators validate transactions, add them to new blocks, and broadcast these blocks to the network. 6. Transaction Finality: BSC achieves fast block times of around 3 seconds and quick transaction finality. This is achieved through the efficient PoSA mechanism that allows validators to rapidly reach consensus. Security and Economic Incentives 7. Staking: Validators are required to stake a substantial amount of BNB, which acts as collateral to ensure their honest behavior. This staked amount can be slashed if validators act maliciously. Staking incentivizes validators to act in the network's best interest to avoid losing their staked BNB. 8. Delegation and Rewards: Delegators earn rewards proportional to their stake in validators. This incentivizes them to choose reliable validators and participate in the network’s security. Validators and delegators share transaction fees as rewards, which provides continuous economic incentives to maintain network security and performance. 9. Transaction Fees: BSC employs low transaction fees, paid in BNB, making it cost-effective for users. These fees are collected by validators as part of their rewards, further incentivizing them to validate transactions accurately and efficiently.
The Ethereum network uses a Proof-of-Stake Consensus Mechanism to validate new transactions on the blockchain. Core Components 1. Validators: Validators are responsible for proposing and validating new blocks. To become a validator, a user must deposit (stake) 32 ETH into a smart contract. This stake acts as collateral and can be slashed if the validator behaves dishonestly. 2. Beacon Chain: The Beacon Chain is the backbone of Ethereum 2.0. It coordinates the network of validators and manages the consensus protocol. It is responsible for creating new blocks, organizing validators into committees, and implementing the finality of blocks. Consensus Process 1. Block Proposal: Validators are chosen randomly to propose new blocks. This selection is based on a weighted random function (WRF), where the weight is determined by the amount of ETH staked. 2. Attestation: Validators not proposing a block participate in attestation. They attest to the validity of the proposed block by voting for it. Attestations are then aggregated to form a single proof of the block’s validity. 3. Committees: Validators are organized into committees to streamline the validation process. Each committee is responsible for validating blocks within a specific shard or the Beacon Chain itself. This ensures decentralization and security, as a smaller group of validators can quickly reach consensus. 4. Finality: Ethereum 2.0 uses a mechanism called Casper FFG (Friendly Finality Gadget) to achieve finality. Finality means that a block and its transactions are considered irreversible and confirmed. Validators vote on the finality of blocks, and once a supermajority is reached, the block is finalized. 5. Incentives and Penalties: Validators earn rewards for participating in the network, including proposing blocks and attesting to their validity. Conversely, validators can be penalized (slashed) for malicious behavior, such as double-signing or being offline for extended periods. This ensures honest participation and network security.
Stimuleringsmechanismen en toepasselijke vergoedingen
Dai Token is present on the following networks: binance_smart_chain, ethereum.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses the Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism to ensure network security and incentivize participation from validators and delegators. Incentive Mechanisms 1. Validators: Staking Rewards: Validators must stake a significant amount of BNB to participate in the consensus process. They earn rewards in the form of transaction fees and block rewards. Selection Process: Validators are selected based on the amount of BNB staked and the votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chances of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. 2. Delegators: Delegated Staking: Token holders can delegate their BNB to validators. This delegation increases the validator's total stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Shared Rewards: Delegators earn a portion of the rewards that validators receive. This incentivizes token holders to participate in the network’s security and decentralization by choosing reliable validators. 3. Candidates: Pool of Potential Validators: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are waiting to become active validators. They ensure that there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, maintaining network resilience. 4. Economic Security: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior or failure to perform their duties. Penalties include slashing a portion of their staked tokens, ensuring that validators act in the best interest of the network. Opportunity Cost: Staking requires validators and delegators to lock up their BNB tokens, providing an economic incentive to act honestly to avoid losing their staked assets. Fees on the Binance Smart Chain 5. Transaction Fees: Low Fees: BSC is known for its low transaction fees compared to other blockchain networks. These fees are paid in BNB and are essential for maintaining network operations and compensating validators. Dynamic Fee Structure: Transaction fees can vary based on network congestion and the complexity of the transactions. However, BSC ensures that fees remain significantly lower than those on the Ethereum mainnet. 6. Block Rewards: Incentivizing Validators: Validators earn block rewards in addition to transaction fees. These rewards are distributed to validators for their role in maintaining the network and processing transactions. 7. Cross-Chain Fees: Interoperability Costs: BSC supports cross-chain compatibility, allowing assets to be transferred between Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain. These cross-chain operations incur minimal fees, facilitating seamless asset transfers and improving user experience. 8. Smart Contract Fees: Deployment and Execution Costs: Deploying and interacting with smart contracts on BSC involves paying fees based on the computational resources required. These fees are also paid in BNB and are designed to be cost-effective, encouraging developers to build on the BSC platform.
Ethereum, particularly after transitioning to Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2), employs a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to secure its network. The incentives for validators and the fee structures play crucial roles in maintaining the security and efficiency of the blockchain. Incentive Mechanisms 1. Staking Rewards: Validator Rewards: Validators are essential to the PoS mechanism. They are responsible for proposing and validating new blocks. To participate, they must stake a minimum of 32 ETH. In return, they earn rewards for their contributions, which are paid out in ETH. These rewards are a combination of newly minted ETH and transaction fees from the blocks they validate. Reward Rate: The reward rate for validators is dynamic and depends on the total amount of ETH staked in the network. The more ETH staked, the lower the individual reward rate, and vice versa. This is designed to balance the network's security and the incentive to participate. 2. Transaction Fees: Base Fee: After the implementation of Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP) 1559, the transaction fee model changed to include a base fee that is burned (i.e., removed from circulation). This base fee adjusts dynamically based on network demand, aiming to stabilize transaction fees and reduce volatility. Priority Fee (Tip): Users can also include a priority fee (tip) to incentivize validators to include their transactions more quickly. This fee goes directly to the validators, providing them with an additional incentive to process transactions efficiently. 3. Penalties for Malicious Behavior: Slashing: Validators face penalties (slashing) if they engage in malicious behavior, such as double-signing or validating incorrect information. Slashing results in the loss of a portion of their staked ETH, discouraging bad actors and ensuring that validators act in the network's best interest. Inactivity Penalties: Validators also face penalties for prolonged inactivity. This ensures that validators remain active and engaged in maintaining the network's security and operation. Fees Applicable on the Ethereum Blockchain 1. Gas Fees: Calculation: Gas fees are calculated based on the computational complexity of transactions and smart contract executions. Each operation on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) has an associated gas cost. Dynamic Adjustment: The base fee introduced by EIP-1559 dynamically adjusts according to network congestion. When demand for block space is high, the base fee increases, and when demand is low, it decreases. 2. Smart Contract Fees: Deployment and Interaction: Deploying a smart contract on Ethereum involves paying gas fees proportional to the contract's complexity and size. Interacting with deployed smart contracts (e.g., executing functions, transferring tokens) also incurs gas fees. Optimizations: Developers are incentivized to optimize their smart contracts to minimize gas usage, making transactions more cost-effective for users. 3. Asset Transfer Fees: Token Transfers: Transferring ERC-20 or other token standards involves gas fees. These fees vary based on the token's contract implementation and the current network demand.
Begin van de periode waarop de informatieverschaffing betrekking heeft
2024-04-20
Einde van de periode waarop de informatie betrekking heeft
2025-04-20
Energierapport
Energieverbruik
38501.82538 (kWh/a)
Energieverbruiksbronnen en -methodologieën
The energy consumption of this asset is aggregated across multiple components:
To determine the energy consumption of a token, the energy consumption of the network(s) binance_smart_chain, ethereum is calculated first. Based on the crypto asset's gas consumption per network, the share of the total consumption of the respective network that is assigned to this asset is defined. When calculating the energy consumption, we used - if available - the Functionally Fungible Group Digital Token Identifier (FFG DTI) to determine all implementations of the asset of question in scope and we update the mappings regulary, based on data of the Digital Token Identifier Foundation.















Socials