AXS
Axie Infinity-pris
$2,3100
-$0,01000
(−0,44 %)
Prisendring fra 00:00 UTC til nå

Ansvarsfraskrivelse
Det sosiale innholdet på denne siden («Innhold»), inkludert, men ikke begrenset til, tweets og statistikk levert av LunarCrush, er hentet fra tredjeparter og levert «som det er» kun for informasjonsformål. OKX garanterer ikke kvaliteten eller nøyaktigheten til innholdet, og innholdet representerer ikke synspunktene til OKX. Det er ikke ment å gi (i) investeringsråd eller anbefalinger, (ii) et tilbud eller oppfordring til å kjøpe, selge eller holde digitale ressurser, eller (iii) finansiell, regnskapsmessig, juridisk eller skattemessig rådgivning. Digitale ressurser, inkludert stablecoins og NFT-er, innebærer en høy grad av risiko, og kan variere mye. Prisen og ytelsen til den digitale ressursen er ikke garantert og kan endres uten varsel.
OKX gir ikke anbefalinger om investering eller aktiva. Du bør vurdere nøye om trading eller holding av digitale aktiva er egnet for deg i lys av din økonomiske situasjon. Rådfør deg med din juridiske / skatte- / investeringsprofesjonelle for spørsmål om dine spesifikke omstendigheter. For ytterligere detaljer, se våre vilkår for bruk og risikoadvarsel. Ved å bruke tredjepartsnettstedet («TPN») godtar du at all bruk av TPN vil være underlagt og styrt av vilkårene på TPN. Med mindre det er uttrykkelig angitt skriftlig, er OKX og dets partnere («OKX») ikke på noen måte knyttet til eieren eller operatøren av TPN. Du godtar at OKX ikke er ansvarlige for tap, skade eller andre konsekvenser som oppstår fra din bruk av TPN. Vær oppmerksom på at bruk av TNS kan føre til tap eller reduksjon av eiendelene dine. Produktet er kanskje ikke tilgjengelig i alle jurisdiksjoner.
OKX gir ikke anbefalinger om investering eller aktiva. Du bør vurdere nøye om trading eller holding av digitale aktiva er egnet for deg i lys av din økonomiske situasjon. Rådfør deg med din juridiske / skatte- / investeringsprofesjonelle for spørsmål om dine spesifikke omstendigheter. For ytterligere detaljer, se våre vilkår for bruk og risikoadvarsel. Ved å bruke tredjepartsnettstedet («TPN») godtar du at all bruk av TPN vil være underlagt og styrt av vilkårene på TPN. Med mindre det er uttrykkelig angitt skriftlig, er OKX og dets partnere («OKX») ikke på noen måte knyttet til eieren eller operatøren av TPN. Du godtar at OKX ikke er ansvarlige for tap, skade eller andre konsekvenser som oppstår fra din bruk av TPN. Vær oppmerksom på at bruk av TNS kan føre til tap eller reduksjon av eiendelene dine. Produktet er kanskje ikke tilgjengelig i alle jurisdiksjoner.
Axie Infinity markedsinformasjon
Markedsverdi
Markedsverdien beregnes ved å multiplisere det sirkulerende tilbudet av en mynt med den siste prisen.
Markedsverdi = Sirkulerende tilbud × Siste pris
Markedsverdi = Sirkulerende tilbud × Siste pris
Sirkulerende forsyning
Totalbeløpet for en mynt som er offentlig tilgjengelig på markedet.
Markedsverdirangering
En mynts rangering i form av markedsverdi.
Historisk toppnivå
Høyeste pris en mynt har nådd i sin handelshistorikk.
Historisk bunnivå
Laveste pris en mynt har nådd i sin handelshistorikk.
Markedsverdi
$384,06 mill.
Sirkulerende forsyning
165 472 442 AXS
61,28 % av
270 000 000 AXS
Markedsverdirangering
--
Revisjoner

Siste revisjon: 21. juni 2022, (UTC+8)
Høyeste pris siste 24 timer
$2,3800
Laveste pris siste 24 timer
$2,2800
Historisk toppnivå
$165,83
−98,61 % (-$163,52)
Sist oppdatert: 7. nov. 2021, (UTC+8)
Historisk bunnivå
$1,9200
+20,31 % (+$0,39000)
Sist oppdatert: 23. juni 2025, (UTC+8)
Hva føler du om AXS i dag?
Del følelsene dine her ved å gi en tommel opp hvis du føler deg optimistisk om mynten eller en tommel ned hvis du føler deg nedadgående.
Stem for å vise resultater
Axie Infinity-feed
Følgende innhold er hentet fra .

slappjakke
Husker du spillerne som hadde hundrevis av tenåringer som spilte Axie Infinity for at de skulle tjene magiske kjærlighetsdrikker?
Ja, det var 4 år siden.
Nå kan du bare trene og spinne opp 100 autonome kodekoperatører for å spille for deg i stedet
... og tjene penger på det og selge det til andre
✅ AI x robotikk
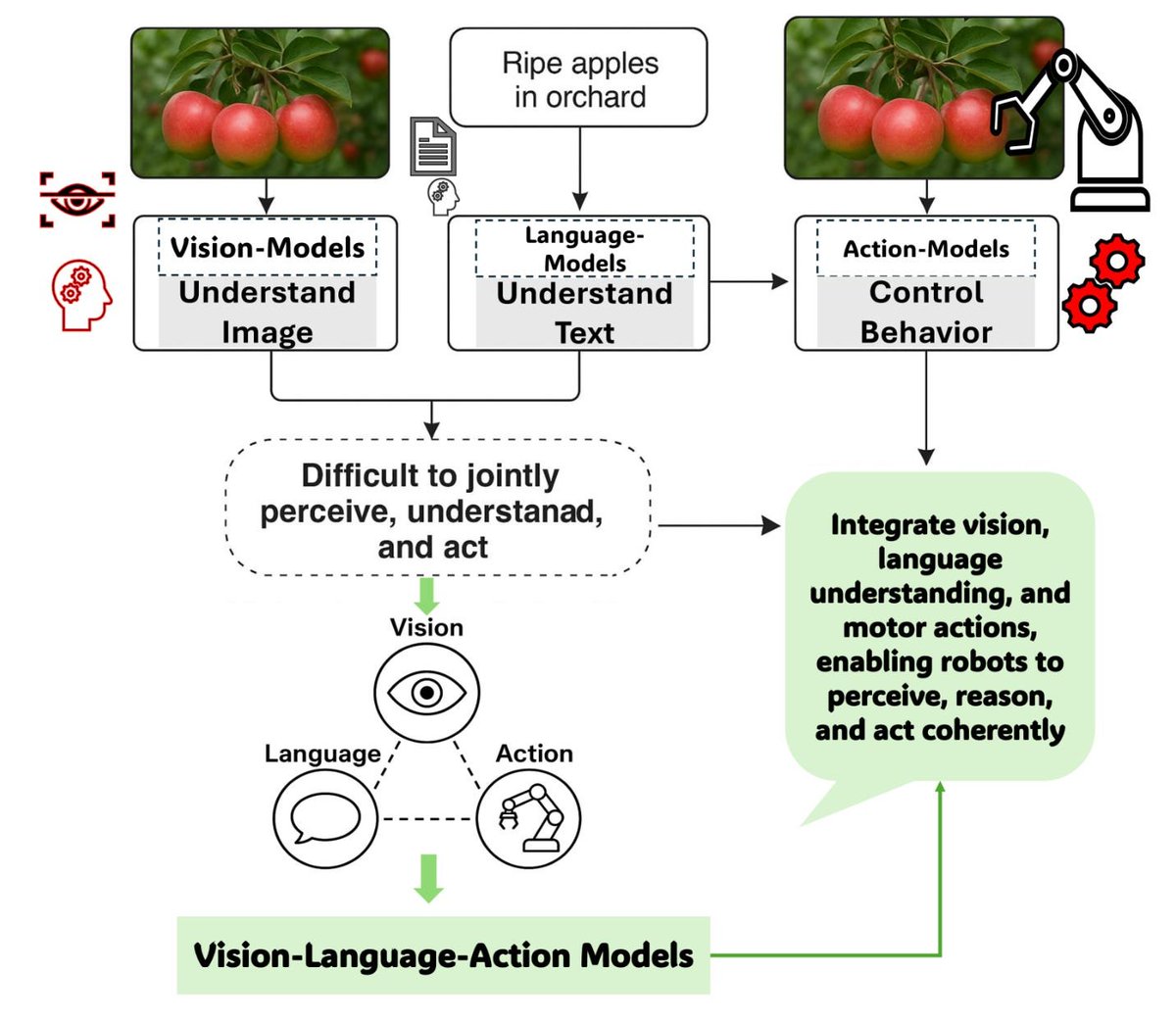
AI x Robotics-fortellingen varmes opp for ordentlig med VLA-modeller
På dette stadiet i AI-økosystemet bruker de fleste protokoller og agenter tekstbaserte LLM-motorer eller statiske skjermbilder for å tolke data
Men bare husk at det meste av den virkelige verden ikke har API-tilgang, du trenger visjon, beslutninger og handlinger. Den virkelige verden må sees i piksler, og det er her VLA-modeller kommer inn
@Codecopenflow muliggjør automatisering av programvare og robotikk gjennom visjon ved hjelp av en teknologistabel bygget fra bunnen av
✅ CODEC-operatører
Operatører er autonome programvareagenter som kan utføre oppgaver gjennom en oppfatte-fornuft-handle-syklus. Muligheten til å se skjermen (eller kamerafeeder eller sensordata) lar dem ta beslutninger LLM-er ikke ville være i stand til å gjøre
• Oppfatning: Tar skjermbilder, kamerafeeder eller sensordata
• Resonnement: Behandler observasjoner og instruksjoner ved hjelp av synsspråkmodeller
• Handling: Utfører beslutninger gjennom UI-interaksjoner eller maskinvarekontroll
I en kontinuerlig sløyfe
Operatørene kan kjøre på bare-metal-servere, virtuelle maskiner (på alle operativsystemer), eller til og med på roboter.
Hver operatør får automatisk en dedikert databehandlingsmaskin (isolert virtuell maskin eller beholderforekomst), og kan sikres med TEE-er (isolering på maskinvarenivå) for sensitiv kode og data.
✅ AI-intelligenslag
Operatørene kan konfigureres til å bruke en eller flere modeller (LLM eller VLA) kombinert som sin "hjerne"
For eksempel, ved å pare den rimelige Mixtral-8×7B-språkmodellen med åpen kildekode CogVLM-visjonsmodellen kan operatører lese tekst på skjermen og tolke live skjerm- eller kamerafeeder - alt til en brøkdel av GPT-4s kostnad.
En VLA-modell (Vision-Language-Action) lar agenten tolke visuelle inndata og deretter bestemme seg for en handling basert på hva den ser
✅ Bruksområder
🔹 Automatisering av skrivebord
Kan automatisere repeterende kontoroppgaver ved å kontrollere GUI-er. Som å fylle ut regneark, oppdatere kalendere eller andre oppgaver som krever GUI-interaksjon
Kan håndtere UI-oppdateringer da den faktisk kan se hva den gjør
🔹 Spillagenter
Operatører kan kontrollere spillere eller teste videospill. Agentene strømmer skjermen og kan utføre handlinger basert på det de ser ved å sende tastatur- eller musekommandoer til spillet.
Kan brukes til QA-testing, eller til og med avanserte NPC-motstandere eller automatisering av web3-spill
🔹 Robotics
Operatører kan kontrollere fysiske roboter. Maskinlaget vil koble seg til en robots maskinvare med sensorer og aktuatorer, og agenten kan sende kommandoer for å bevege en arm eller navigere.
For eksempel kan den fange en kamerafeed av objekter som beveger seg på et transportbånd og gjøre handlinger basert på bevegelsen. Hvis det er en hindring i veien, kan operatøren se den og kontrollere roboten for å unngå den
✅ Datainnsamling og Onchain sikkerhetsskinner
Ved å bringe informasjonen om operatørene onchain til Solana, kan de tilby uforanderlige handlingslogger fra alle handlinger som utføres
I fremtiden kan vi se et punkt der robotselskaper vil bli pålagt å satse et token for å garantere at operatørene deres ikke vil få en robot til å ta fysisk kontakt med et menneske over en viss kraft. Hvis de bryter det, vil de bli kuttet for en del av det stakede tokenet (som EigenLayer / Symbiotic restaking)
✅ Opplæringsmiljø for robotikk
Med Codec kan utrente virtuelle modeller distribueres til et dynamisk treningsområde med høy kvalitet, uten behov for fysisk robot.
Simuler, lær opp og finjuster kompleks atferd i skyskala, og overfør deretter disse policyene til ekte maskinvare med tillit.
Treningsmiljøer kan raskt spinnes opp for alle typer operatører (programvare, spill eller robotikk)
✅ SDK for kodek
En fullstendig SDK og API er utviklet slik at utviklere enkelt kan distribuere operatørene sine
✅ Markedsplass for operatører
Operatører kan (i fremtiden) selges på en tilpasset markedsplass.
Det vil være en inntektsdeling slik at du kan sende og tjene penger på VLA-operatøren din, noe som betyr at hvis du trener effektive operatører, kan du ha ekstra inntektsstrømmer
✅ Avsluttende tanker
Jeg tror vi vil se en massiv utvikling på VLA-feltet i løpet av det neste året. Vi har sett hvor raskt LLM-er utvikles, det var bare noen få år siden GPT-1 ble lansert. Robotikk og synsmodeller vil med stor sannsynlighet bli en het fortelling på et tidspunkt i denne syklusen, og jeg liker å bli posisjonert tidlig
Åh, og nevnte jeg at medgründerne er fra Hugging Face og Elixir-spill 👀
Merk: Slappjakke har store $CODEC vesker, og dette er en av de gangene jeg ble enda mer bullish mens jeg skrev denne tråden og la til enda flere
Dette er som alltid ikke økonomisk rådgivning og en høyrisikoinvestering, så gjør din egen research.
Vis originalen

6,18k
82
Konverter USD til AXS


Axie Infinity prisutvikling i USD
Gjeldende pris på Axie Infinity er $2,3100. Siden 00:00 UTC, Axie Infinity har redusert ved −0,43 %. Den har for tiden en sirkulerende forsyning på 165 472 442 AXS og en maksimal forsyning på 270 000 000 AXS, noe som gir den en fullt utvannet markedsverdi på $384,06 mill.. For tiden har Axie Infinity-mynten 0. plass i markedsverdirangeringen. Axie Infinity/USD-prisen oppdateres i sanntid.
I dag
-$0,01000
−0,44 %
7 dager
+$0,15300
+7,09 %
30 dager
-$0,27600
−10,68 %
3 måneder
-$0,45300
−16,40 %
Populære Axie Infinity konverteringer
Sist oppdatert: 04.07.2025, 06:55
| 1 AXS til USD | 2,3210 $ |
| 1 AXS til EUR | 1,9741 € |
| 1 AXS til PHP | 130,83 ₱ |
| 1 AXS til IDR | 37 672,46 Rp |
| 1 AXS til GBP | 1,6997 £ |
| 1 AXS til CAD | 3,1526 $ |
| 1 AXS til AED | 8,5250 AED |
| 1 AXS til VND | 60 806,92 ₫ |
Om Axie Infinity (AXS)
Den oppgitte vurderingen er en samlet vurdering som OKX har samlet inn fra de oppgitte kildene, og er kun ment som informasjon. OKX garanterer ikke for kvaliteten eller nøyaktigheten av vurderingene. Denne aktiviteten er ikke ment å gi (i) investeringsråd eller en anbefaling, (ii) et tilbud eller oppfordring om å kjøpe, selge eller holde digitale ressurser, eller (iii) finansiell, regnskapsmessig, juridisk eller skattemessig rådgivning. Digitale ressurser, inkludert stablecoins og NFT-er, innebærer en høy grad av risiko, og verdien kan variere mye, og til og med verdiløs. Prisen og ytelsen til digitale ressurser er ikke garantert og kan endres uten varsel. De digital ressursene dine er ikke dekket av forsikring mot potensielle tap. Historisk avkastning er ikke en indikasjon på fremtidig avkastning. OKX garanterer ikke avkastning, tilbakebetaling av hovedstol eller renter. OKX gir ikke anbefalinger om investeringer eller aktiva. Du bør nøye overveie om trading eller holding digitale ressurser passer for deg i lys av din økonomiske situasjon. Rådfør deg med din advokat/skatte- eller investeringsekspert hvis du har spørsmål om dine spesifikke forhold.
Vis mer
- Offisiell nettside
- White Paper
- Blokkutforsker
Om tredjepartsnettsteder
Om tredjepartsnettsteder
Ved å bruke tredjepartsnettstedet ("TPW") godtar du at all bruk av TPW vil være underlagt og styrt av vilkårene i TPW. Med mindre det er uttrykkelig angitt skriftlig, er OKX og dets tilknyttede selskaper ("OKX") ikke på noen måte knyttet til eieren eller operatøren av TPW. Du godtar at OKX ikke er ansvarlig eller ansvarlig for tap, skade eller andre konsekvenser som oppstår fra din bruk av TPW. Vær oppmerksom på at bruk av en TPW kan føre til tap eller reduksjon av dine aktiva.
Axie Infinity Vanlige spørsmål
Hvor mye er 1 Axie Infinity verdt i dag?
For øyeblikket er en Axie Infinity verdt $2,3100. For svar og innsikt i prishandlingen til Axie Infinity, er du på rett sted. Utforsk de nyeste Axie Infinity diagrammene og trade ansvarlig med OKX.
Hva er kryptovaluta?
Kryptovalutaer, for eksempel Axie Infinity, er digitale eiendeler som opererer på en offentlig hovedbok kalt blokk-kjeder. Lær mer om mynter og tokens som tilbys på OKX og deres forskjellige attributter, som inkluderer live-priser og sanntidsdiagrammer.
Når ble kryptovaluta oppfunnet?
Takket være finanskrisen i 2008 økte interessen for desentralisert finans. Bitcoin tilbød en ny løsning ved å være en sikker digital ressurs på et desentralisert nettverk. Siden den gang har mange andre tokens som Axie Infinity blitt opprettet også.
Vil prisen på Axie Infinity gå opp i dag?
Ta en titt på vår Axie Infinity prisantydningsside for å forutsi fremtidige priser og bestemme prismålene dine.
ESG-erklæring
ESG-forskrifter (Environmental, Social, and Governance) for kryptoaktiva tar sikte på å adressere deres miljøpåvirkning (f.eks. energikrevende gruvedrift), fremme åpenhet og sikre etisk styringspraksis for å tilpasse kryptoindustrien med bredere bærekraft- og samfunnsmål. Disse forskriftene oppfordrer til overholdelse av standarder som reduserer risiko og fremmer tillit til digitale eiendeler.
Aktivadetaljer
Navn
OKCoin Europe Ltd
Relevant juridisk enhetsidentifikator
54930069NLWEIGLHXU42
Navn på kryptoaktiva
Axie Infinity Shard
Konsensusmekanisme
Axie Infinity Shard is present on the following networks: Binance Smart Chain, Ethereum, Harmony One, Ronin, Solana.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses a hybrid consensus mechanism called Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA), which combines elements of Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA). This method ensures fast block times and low fees while maintaining a level of decentralization and security. Core Components 1. Validators (so-called “Cabinet Members”): Validators on BSC are responsible for producing new blocks, validating transactions, and maintaining the network’s security. To become a validator, an entity must stake a significant amount of BNB (Binance Coin). Validators are selected through staking and voting by token holders. There are 21 active validators at any given time, rotating to ensure decentralization and security. 2. Delegators: Token holders who do not wish to run validator nodes can delegate their BNB tokens to validators. This delegation helps validators increase their stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Delegators earn a share of the rewards that validators receive, incentivizing broad participation in network security. 3. Candidates: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are in the pool waiting to become validators. They are essentially potential validators who are not currently active but can be elected to the validator set through community voting. Candidates play a crucial role in ensuring there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, thus maintaining network resilience and decentralization. Consensus Process 4. Validator Selection: Validators are chosen based on the amount of BNB staked and votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chance of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. The selection process involves both the current validators and the pool of candidates, ensuring a dynamic and secure rotation of nodes. 5. Block Production: The selected validators take turns producing blocks in a PoA-like manner, ensuring that blocks are generated quickly and efficiently. Validators validate transactions, add them to new blocks, and broadcast these blocks to the network. 6. Transaction Finality: BSC achieves fast block times of around 3 seconds and quick transaction finality. This is achieved through the efficient PoSA mechanism that allows validators to rapidly reach consensus. Security and Economic Incentives 7. Staking: Validators are required to stake a substantial amount of BNB, which acts as collateral to ensure their honest behavior. This staked amount can be slashed if validators act maliciously. Staking incentivizes validators to act in the network's best interest to avoid losing their staked BNB. 8. Delegation and Rewards: Delegators earn rewards proportional to their stake in validators. This incentivizes them to choose reliable validators and participate in the network’s security. Validators and delegators share transaction fees as rewards, which provides continuous economic incentives to maintain network security and performance. 9. Transaction Fees: BSC employs low transaction fees, paid in BNB, making it cost-effective for users. These fees are collected by validators as part of their rewards, further incentivizing them to validate transactions accurately and efficiently.
The crypto-asset's Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, introduced with The Merge in 2022, replaces mining with validator staking. Validators must stake at least 32 ETH every block a validator is randomly chosen to propose the next block. Once proposed the other validators verify the blocks integrity. The network operates on a slot and epoch system, where a new block is proposed every 12 seconds, and finalization occurs after two epochs (~12.8 minutes) using Casper-FFG. The Beacon Chain coordinates validators, while the fork-choice rule (LMD-GHOST) ensures the chain follows the heaviest accumulated validator votes. Validators earn rewards for proposing and verifying blocks, but face slashing for malicious behavior or inactivity. PoS aims to improve energy efficiency, security, and scalability, with future upgrades like Proto-Danksharding enhancing transaction efficiency.
Harmony operates on a consensus mechanism called Effective Proof of Stake (EPoS), designed to balance validator influence and enhance network security while improving transaction scalability. Core Components: 1. Effective Proof of Stake (EPoS): Validator Diversity: EPoS allows a large number of validators to participate and limits the influence of high-stake validators, promoting decentralization and preventing stake centralization. Staking Across Shards: Multiple validators compete within each shard, distributing staking power more broadly and enhancing network security. 2. Sharding with PBFT Finality: Parallel Transaction Processing: Harmony’s four shards enable independent processing of transactions and smart contracts, enhancing scalability and throughput. Fast Finality with PBFT: Each shard uses a modified Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) model, ensuring immediate finality once blocks are validated and achieving high transaction speeds.
Ronin utilizes a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, where community-elected validators are responsible for securing the network and validating transactions. Core Components of Ronin’s Consensus: 1. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Community Voting for Validator Selection: RON token holders delegate their tokens to vote for validators, who are then selected to produce blocks, validate transactions, and maintain network security. Validators with the most votes are chosen to participate in consensus. Periodic Validator Rotation: Validators are regularly rotated based on community votes, enhancing decentralization and preventing long-term control by any single validator group. This rotation supports both security and fairness. 2. Incentive-Driven Voting System: Alignment with Community Interests: The voting system ensures that validators remain aligned with community goals. Validators that fail to perform adequately or act against network interests may lose votes and be replaced by more trusted participants.
Solana uses a unique combination of Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to achieve high throughput, low latency, and robust security. Here’s a detailed explanation of how these mechanisms work: Core Concepts 1. Proof of History (PoH): Time-Stamped Transactions: PoH is a cryptographic technique that timestamps transactions, creating a historical record that proves that an event has occurred at a specific moment in time. Verifiable Delay Function: PoH uses a Verifiable Delay Function (VDF) to generate a unique hash that includes the transaction and the time it was processed. This sequence of hashes provides a verifiable order of events, enabling the network to efficiently agree on the sequence of transactions. 2. Proof of Stake (PoS): Validator Selection: Validators are chosen to produce new blocks based on the number of SOL tokens they have staked. The more tokens staked, the higher the chance of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. Delegation: Token holders can delegate their SOL tokens to validators, earning rewards proportional to their stake while enhancing the network's security. Consensus Process 1. Transaction Validation: Transactions are broadcast to the network and collected by validators. Each transaction is validated to ensure it meets the network’s criteria, such as having correct signatures and sufficient funds. 2. PoH Sequence Generation: A validator generates a sequence of hashes using PoH, each containing a timestamp and the previous hash. This process creates a historical record of transactions, establishing a cryptographic clock for the network. 3. Block Production: The network uses PoS to select a leader validator based on their stake. The leader is responsible for bundling the validated transactions into a block. The leader validator uses the PoH sequence to order transactions within the block, ensuring that all transactions are processed in the correct order. 4. Consensus and Finalization: Other validators verify the block produced by the leader validator. They check the correctness of the PoH sequence and validate the transactions within the block. Once the block is verified, it is added to the blockchain. Validators sign off on the block, and it is considered finalized. Security and Economic Incentives 1. Incentives for Validators: Block Rewards: Validators earn rewards for producing and validating blocks. These rewards are distributed in SOL tokens and are proportional to the validator’s stake and performance. Transaction Fees: Validators also earn transaction fees from the transactions included in the blocks they produce. These fees provide an additional incentive for validators to process transactions efficiently. 2. Security: Staking: Validators must stake SOL tokens to participate in the consensus process. This staking acts as collateral, incentivizing validators to act honestly. If a validator behaves maliciously or fails to perform, they risk losing their staked tokens. Delegated Staking: Token holders can delegate their SOL tokens to validators, enhancing network security and decentralization. Delegators share in the rewards and are incentivized to choose reliable validators. 3. Economic Penalties: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior, such as double-signing or producing invalid blocks. This penalty, known as slashing, results in the loss of a portion of the staked tokens, discouraging dishonest actions.
Insentivmekanismer og gjeldende gebyrer
Axie Infinity Shard is present on the following networks: Binance Smart Chain, Ethereum, Harmony One, Ronin, Solana.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) uses the Proof of Staked Authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism to ensure network security and incentivize participation from validators and delegators. Incentive Mechanisms 1. Validators: Staking Rewards: Validators must stake a significant amount of BNB to participate in the consensus process. They earn rewards in the form of transaction fees and block rewards. Selection Process: Validators are selected based on the amount of BNB staked and the votes received from delegators. The more BNB staked and votes received, the higher the chances of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. 2. Delegators: Delegated Staking: Token holders can delegate their BNB to validators. This delegation increases the validator's total stake and improves their chances of being selected to produce blocks. Shared Rewards: Delegators earn a portion of the rewards that validators receive. This incentivizes token holders to participate in the network’s security and decentralization by choosing reliable validators. 3. Candidates: Pool of Potential Validators: Candidates are nodes that have staked the required amount of BNB and are waiting to become active validators. They ensure that there is always a sufficient pool of nodes ready to take on validation tasks, maintaining network resilience. 4. Economic Security: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior or failure to perform their duties. Penalties include slashing a portion of their staked tokens, ensuring that validators act in the best interest of the network. Opportunity Cost: Staking requires validators and delegators to lock up their BNB tokens, providing an economic incentive to act honestly to avoid losing their staked assets. Fees on the Binance Smart Chain 5. Transaction Fees: Low Fees: BSC is known for its low transaction fees compared to other blockchain networks. These fees are paid in BNB and are essential for maintaining network operations and compensating validators. Dynamic Fee Structure: Transaction fees can vary based on network congestion and the complexity of the transactions. However, BSC ensures that fees remain significantly lower than those on the Ethereum mainnet. 6. Block Rewards: Incentivizing Validators: Validators earn block rewards in addition to transaction fees. These rewards are distributed to validators for their role in maintaining the network and processing transactions. 7. Cross-Chain Fees: Interoperability Costs: BSC supports cross-chain compatibility, allowing assets to be transferred between Binance Chain and Binance Smart Chain. These cross-chain operations incur minimal fees, facilitating seamless asset transfers and improving user experience. 8. Smart Contract Fees: Deployment and Execution Costs: Deploying and interacting with smart contracts on BSC involves paying fees based on the computational resources required. These fees are also paid in BNB and are designed to be cost-effective, encouraging developers to build on the BSC platform.
The crypto-asset's PoS system secures transactions through validator incentives and economic penalties. Validators stake at least 32 ETH and earn rewards for proposing blocks, attesting to valid ones, and participating in sync committees. Rewards are paid in newly issued ETH and transaction fees. Under EIP-1559, transaction fees consist of a base fee, which is burned to reduce supply, and an optional priority fee (tip) paid to validators. Validators face slashing if they act maliciously and incur penalties for inactivity. This system aims to increase security by aligning incentives while making the crypto-asset's fee structure more predictable and deflationary during high network activity.
Harmony incentivizes validators and delegators to participate in network security and performance through staking rewards, transaction fees, and a unique reward structure promoting decentralization. Incentive Mechanisms: 1. Staking Rewards for Validators and Delegators: ONE Token Rewards: Validators earn ONE tokens for validating transactions and securing the network, with a share of these rewards distributed to delegators based on the amount staked. 2. Decentralization Penalty for High Stake: Reward Adjustment for Large Stakeholders: Validators with an excessive delegated stake experience reduced rewards, preventing centralization and encouraging a fair distribution of staking power. Applicable Fees: 1. Transaction Fees: Low-Cost Transactions in ONE: Harmony charges minimal transaction fees in ONE tokens, benefiting high-frequency applications and providing validators with additional rewards.
Ronin’s incentive model combines rewards, slashing mechanisms, and governance features to support network security and encourage active community participation. Incentive Mechanisms: 1. Rewards for Validators and Delegators: Staking Rewards for Validators: Validators earn RON tokens as rewards for successfully producing blocks and validating transactions. These rewards incentivize validators to fulfill their duties diligently, maintaining network stability. Delegator Rewards: Delegators who stake their tokens with selected validators also earn a portion of the staking rewards. This sharing of rewards promotes broad participation from token holders in network security and governance. 2. Slashing Mechanism for Accountability: Penalty for Malicious Behavior: A slashing mechanism penalizes validators who act dishonestly or fail to meet performance standards by cutting a portion of their staked RON tokens. This deters misbehavior and encourages responsible participation. Delegator Risk: Delegators who stake with misbehaving validators are also subject to slashing, which encourages them to choose trustworthy validators and monitor performance carefully. 3. Governance Participation: RON Token for Governance: Beyond staking and transaction fees, the RON token enables token holders to participate in governance. This includes voting on network upgrades, validator selection, and other protocol decisions, giving token holders a voice in network direction and policy. Applicable Fees: • Transaction Fees: Fees are paid in RON tokens, contributing to validator rewards and helping to maintain network operations. These fees are designed to be affordable, ensuring accessibility for users while supporting validators’ roles.
Solana uses a combination of Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to secure its network and validate transactions. Here’s a detailed explanation of the incentive mechanisms and applicable fees: Incentive Mechanisms 4. Validators: Staking Rewards: Validators are chosen based on the number of SOL tokens they have staked. They earn rewards for producing and validating blocks, which are distributed in SOL. The more tokens staked, the higher the chances of being selected to validate transactions and produce new blocks. Transaction Fees: Validators earn a portion of the transaction fees paid by users for the transactions they include in the blocks. This provides an additional financial incentive for validators to process transactions efficiently and maintain the network's integrity. 5. Delegators: Delegated Staking: Token holders who do not wish to run a validator node can delegate their SOL tokens to a validator. In return, delegators share in the rewards earned by the validators. This encourages widespread participation in securing the network and ensures decentralization. 6. Economic Security: Slashing: Validators can be penalized for malicious behavior, such as producing invalid blocks or being frequently offline. This penalty, known as slashing, involves the loss of a portion of their staked tokens. Slashing deters dishonest actions and ensures that validators act in the best interest of the network. Opportunity Cost: By staking SOL tokens, validators and delegators lock up their tokens, which could otherwise be used or sold. This opportunity cost incentivizes participants to act honestly to earn rewards and avoid penalties. Fees Applicable on the Solana Blockchain 7. Transaction Fees: Low and Predictable Fees: Solana is designed to handle a high throughput of transactions, which helps keep fees low and predictable. The average transaction fee on Solana is significantly lower compared to other blockchains like Ethereum. Fee Structure: Fees are paid in SOL and are used to compensate validators for the resources they expend to process transactions. This includes computational power and network bandwidth. 8. Rent Fees: State Storage: Solana charges rent fees for storing data on the blockchain. These fees are designed to discourage inefficient use of state storage and encourage developers to clean up unused state. Rent fees help maintain the efficiency and performance of the network. 9. Smart Contract Fees: Execution Costs: Similar to transaction fees, fees for deploying and interacting with smart contracts on Solana are based on the computational resources required. This ensures that users are charged proportionally for the resources they consume.
Starten på perioden som erklæringen gjelder for
2024-07-02
Slutten på perioden som erklæringen gjelder for
2025-07-02
Energirapport
Energiforbruk
1123.97509 (kWh/a)
Energiforbrukskilder og metodologier
The energy consumption of this asset is aggregated across multiple components:
To determine the energy consumption of a token, the energy consumption of the network(s) binance_smart_chain, ethereum, harmony_one, ronin, solana is calculated first. For the energy consumption of the token, a fraction of the energy consumption of the network is attributed to the token, which is determined based on the activity of the crypto-asset within the network. When calculating the energy consumption, the Functionally Fungible Group Digital Token Identifier (FFG DTI) is used - if available - to determine all implementations of the asset in scope. The mappings are updated regularly, based on data of the Digital Token Identifier Foundation. The information regarding the hardware used and the number of participants in the network is based on assumptions that are verified with best effort using empirical data. In general, participants are assumed to be largely economically rational. As a precautionary principle, we make assumptions on the conservative side when in doubt, i.e. making higher estimates for the adverse impacts.
Konverter USD til AXS




















